The Evolution of Blockchain Development: Unlocking the Future
Blockchain development is being seen as an innovative technology with the potential to transform industries across the globe. Blockchain development offers safe, transparent, and decentralized solutions for a variety of applications by utilizing the power of distributed ledger technology. Blockchain development has attracted a lot of interest and has turned into a hub of innovation across industries, from healthcare and identity verification to financial transactions and supply chain management. This guide will give you a fundamental grasp of blockchain development and its important advantages and problems, whether you are a technology enthusiast or a business expert looking to comprehend the possibilities of blockchain. 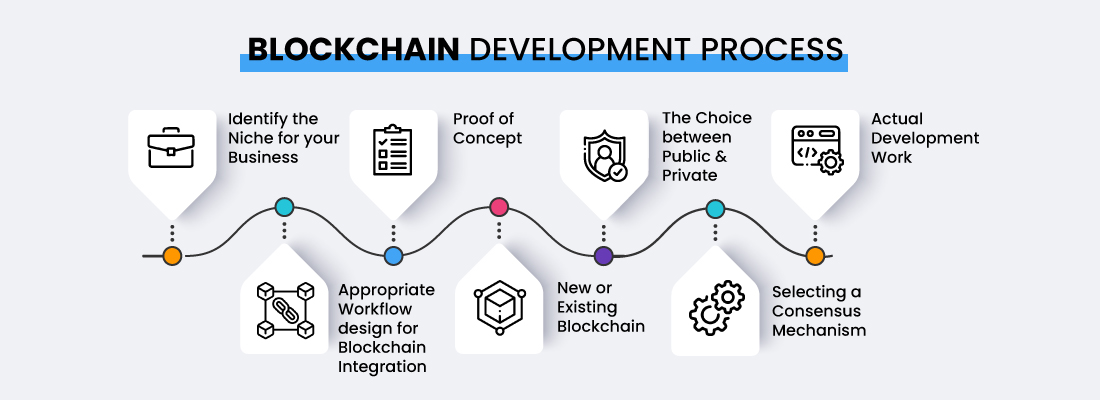
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain development is the method of creating and implementing applications, platforms, or solutions that utilize blockchain technology. It includes creating the framework of the blockchain network, developing smart contracts, establishing consensus mechanisms, and building decentralized and secure systems. Blockchain development intends to revolutionize numerous sectors by utilizing the special qualities of blockchain, like transparency, immutability, and decentralization. It involves knowledge of distributed systems and cryptography, as well as blockchain protocols and programming languages like Solidity for creating smart contracts. Developers can create cutting-edge solutions that improve trust, security, effectiveness, and data integrity in industries like finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more by utilizing the potential of blockchain.
Blockchain development benefits
- Decentralization: Blockchain works on a distributed system of computers called nodes, in which each node keeps a copy of the blockchain. With no need for a central authority or middleman, this decentralized structure offers security, and transparency, and lowers the possibility of a single point of failure.
- Immutability and Transparency: Blockchain is intended to be an immutable and open digital record. Data cannot be readily changed or erased after it has been stored on the blockchain. Verifiable transactions and audit trails are made possible by this feature, which also improves participant trust.
- Enhanced Security: To guarantee the integrity and security of data, blockchain makes use of cryptographic techniques and consensus procedures. Transactions are securely documented and validated, making it difficult for malicious actors to interfere with the data stored on the blockchain.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Blockchain removes the requirement for intermediaries in many processes, decreasing administrative overhead and associated costs. By automating procedures and streamlining transactions, smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain, improve operational efficiency.
- Increased Data Integrity: Due to the immutability of blockchain documents, data stored on the blockchain is extremely susceptible to fraud or unauthorized modifications. This feature is especially valuable in industries where data integrity is vital, like supply chain management, medical care, or finance.
- Improved Traceability and Auditability: Blockchain offers an accessible and traceable record of transactions. Each transaction is connected to the previous one, developing an audit trail that can be readily verified. Traceability is important in sectors like logistics, food safety, and intellectual property, hence the characteristic is advantageous.
- Disintermediation and trust: Blockchain technology facilitates trust between participants without the use of middlemen. Blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions and encourages direct communication and collaboration between parties by reducing the dependency on central authorities.
- Potential for Innovation: The development of new business models and decentralized applications (DApps) is now possible thanks to the blockchain. It has enabled the establishment of cryptocurrencies, tokenization of assets, and the establishment of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, among other breakthroughs.
Challenges in blockchain development
- Scalability: One of the main problems with blockchain is its inability to grow. The size of the blockchain and the necessary processing power can become an issue as the number of transactions rises. Many blockchain initiatives are actively working to solve the challenging problem of achieving high transaction throughput without sacrificing decentralization.
- Interoperability: Blockchain ecosystems are frequently dispersed, with many blockchain protocols and platforms running separately. It is difficult to achieve interoperability across these various systems since doing so calls for standardization and compatibility requirements that guarantee smooth data transmission and communication between blockchains.
- Governance and Consensus: To verify transactions and uphold the blockchain's integrity, blockchain networks often need a consensus mechanism. It can be difficult to select a governance model and consensus mechanism that are compatible with the network's objectives and needs. The trade-offs between security, scalability, energy efficiency, and decentralization vary depending on the consensus process.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: The decentralized nature of the blockchain system raises regulatory and legal issues. Governments and regulatory organizations are still developing structures for dealing with issues like data privacy, managing identities, taxation, and compliance within the context of blockchain. Getting these regulatory landscapes can be complicated for blockchain developers and companies.
- Security flaws: Although blockchain is thought to be secure, flaws might nevertheless appear at different places across the system. For instance, smart contracts may contain coding mistakes or be vulnerable to malicious assaults, resulting in monetary losses. Additionally, the security and immutability of the blockchain are threatened by 51% of attacks, in which one entity gets control of the majority of the network's computational power.
- User Experience and Adoption: The user experience of blockchain programs can be an obstacle to widespread use. Blockchain connections and interactions can be complex for people with no technical expertise, and the lack of user-friendly applications and simple user interfaces may restrict the accessibility and ease of use of blockchain technology.
FAQs
What are the most popular programming languages for creating blockchains?
Several computer languages, including Solidity (for Ethereum), C++, JavaScript, Python, and Go, are frequently used in the creation of blockchains. The blockchain platform and the particular needs of the project determine the programming language to use.
What are smart agreements, and how are they created?
Self-executing contracts known as "smart contracts" are agreements with set rules and conditions that are maintained on a blockchain. They automatically carry out and uphold an agreement's provisions. Usually created in programming languages like Solidity, smart contracts are implemented on the blockchain platform.
Final thoughts
The development of blockchain technology has become a disruptive force, delivering solutions that improve efficiency, security, and transparency across industries. Blockchain technology promotes trust and eliminates the need for middlemen in a number of processes through the use of decentralised networks, smart contracts, and cryptographic methods. Blockchain development is still evolving and innovating despite obstacles including scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance. Its potential effects can be significant, affecting everything from identity management and healthcare to financial systems and supply chains.
